Other
Performance of Large Language Models as a Resource for Atrial Fibrillation Patients and Providers
Nitin Kondamudi, MD – Electrophysiology Fellow, University of Washington; Fima Macheret, MD – Electrophysiology Fellow, University of Washington; Yaacoub Chahine, MD – Internal Medicine Resident, University of Washington; Nazem Akoum, MD – Section head of Cardiac Electrophysiology, University of Washington
Purpose: We sought to assess the accuracy of LLMs as a source of information about atrial fibrillation (AF) for pts and providers according to the 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS guidelines, along with the utilization of LLM in summarizing contemporary clinical trials (CCTs).
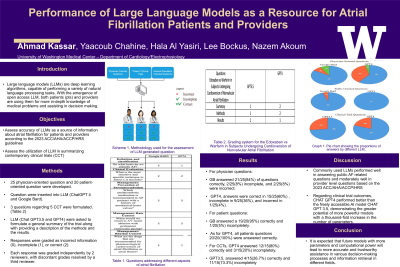
Material and Methods: General population questions covered general AF care, while physician questions covered definitions, classifications, and clinical evaluation, and management. Both were entered into LLM (GPT4 and Google Bard (GB)). Next, we presented LLMs (GPT4 and 3.5) with 15 questions related to 5 AF-related CCT. Responses were graded as incorrect information (0), incomplete (1), or correct (2). Each response was graded independently by 2 reviewers, with discordant grades resolved by a third reviewer. All reviewers were electrophysiology fellows, physicians, or research fellows.) who were blinded to the LLM used (panel A and B).
Results: For physician questions, GB answered 21/25(84%) of questions correctly, 2/25(8%) incomplete, and 2/25(8%) were incorrect. GPT4, answers were correct in 15/25(60%) , incomplete in 9/25(36%), and incorrect in 1/25(4%). For patient questions, GB answered a 19/20(95%) correctly and 1/20(5%) incompletely. As for GPT4, all patients questions 20/20(100%) were answered correctly. For CCTs, GPT4 answered 12/15(80%) correctly and 3/15(20%) incompletely. GPT3.5, answered 4/15(26.7%) correctly and 11/15(73.3%) incompletely (panel C).
Conclusions: We found clear differences in the performance of LLMs in patient and provider AF-related questions. Care providers and pts should be aware of these as the use of LLMs is anticipated to increase.
Material and Methods: General population questions covered general AF care, while physician questions covered definitions, classifications, and clinical evaluation, and management. Both were entered into LLM (GPT4 and Google Bard (GB)). Next, we presented LLMs (GPT4 and 3.5) with 15 questions related to 5 AF-related CCT. Responses were graded as incorrect information (0), incomplete (1), or correct (2). Each response was graded independently by 2 reviewers, with discordant grades resolved by a third reviewer. All reviewers were electrophysiology fellows, physicians, or research fellows.) who were blinded to the LLM used (panel A and B).
Results: For physician questions, GB answered 21/25(84%) of questions correctly, 2/25(8%) incomplete, and 2/25(8%) were incorrect. GPT4, answers were correct in 15/25(60%) , incomplete in 9/25(36%), and incorrect in 1/25(4%). For patient questions, GB answered a 19/20(95%) correctly and 1/20(5%) incompletely. As for GPT4, all patients questions 20/20(100%) were answered correctly. For CCTs, GPT4 answered 12/15(80%) correctly and 3/15(20%) incompletely. GPT3.5, answered 4/15(26.7%) correctly and 11/15(73.3%) incompletely (panel C).
Conclusions: We found clear differences in the performance of LLMs in patient and provider AF-related questions. Care providers and pts should be aware of these as the use of LLMs is anticipated to increase.
