Other
Incidence of Ventricular Dyssynchrony as Assessed by Global Longitudinal Strain with Leadless vs Transvenous Pacemakers
Purpose: Frequent right ventricular (RV) pacing with transvenous pacemakers (TVP) is associated with pacing induced cardiomyopathy (PICM) in a subset of patients. Recent studies have suggested a significantly lower incidence of PICM with leadless pacemakers (LP), but the underlying mechanism is not well understood. The purpose of this study was to assess the incidence of ventricular dyssynchrony, as assessed by global longitudinal strain (GLS), among pacemaker dependent patients with LP vs TVP.
Material and Methods: This retrospective single center study included consecutive pacing dependent patients with LVEF ≥50% at time of implant. The primary endpoints were RV and LV GLS, as assessed by speckle-tracking echocardiography, pre- and post- pacemaker implantation. The secondary endpoints were change in RV and LV GLS after pacemaker implantation and incidence of PICM (defined as a ≥10% reduction in LVEF with an LVEF < 50% after pacemaker implantation).
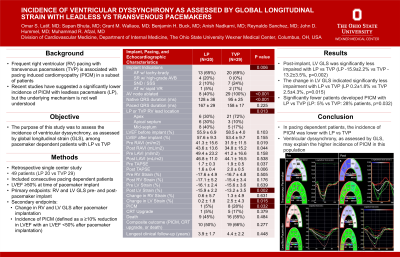
Results: 49 patients (LP 20 vs TVP 29) underwent pacemaker implantation with suitable echocardiographic images for analysis. LP were implanted 30%, 30%, and 40% vs TVP RV leads were implanted 72%, 10%, and 17% at the apex, apical septum and mid-septum respectfully (p=0.013). Baseline LVEF was comparable (LP: 56±7% vs TVP: 58±4%, p=0.103). Paced QRS duration was comparable (LP: 167±29 ms vs TVP: 158±17 ms, p=0.225). At baseline, RV and LV GLS were comparable [(RV pre: LP -17.6±4.9% vs TVP -16.7±4.8%, p=0.505), (LV pre: LP -16.1±2.4% vs TVP -15.6±3.6%, p=0.639)]. However, after pacemaker implantation, RV GLS was comparable, but LV GLS was significantly less impaired with LP vs TVP [(RV post: LP -17.1±5.2% vs TVP -15.4±3.4%, p=0.176), (LV post: LP -15.9±2.2% vs TVP -13.2±3.5%, p=0.002)]. The change in RV GLS was comparable, but the change in LV GLS indicated significantly less impairment with LP vs TVP [(RV change: LP 0.6±5.7% vs TVP 1.3±4.9%, p=0.631), (LV change: LP 0.2±1.8% vs TVP 2.5±4.3%, p=0.015)]. Significantly fewer patients developed PICM with LP vs TVP (LP: 1 (5%) vs TVP: 8 (28%) patients, p=0.032).
Conclusions: In pacemaker dependent patients, the incidence of PICM was lower with LP vs TVP. Despite a similar baseline LV GLS, patients with LP vs TVP had significantly better LV GLS post-pacemaker implant. Ventricular dyssynchrony, as assessed by GLS, may explain the higher incidence of PICM in this population.
Material and Methods: This retrospective single center study included consecutive pacing dependent patients with LVEF ≥50% at time of implant. The primary endpoints were RV and LV GLS, as assessed by speckle-tracking echocardiography, pre- and post- pacemaker implantation. The secondary endpoints were change in RV and LV GLS after pacemaker implantation and incidence of PICM (defined as a ≥10% reduction in LVEF with an LVEF < 50% after pacemaker implantation).
Results: 49 patients (LP 20 vs TVP 29) underwent pacemaker implantation with suitable echocardiographic images for analysis. LP were implanted 30%, 30%, and 40% vs TVP RV leads were implanted 72%, 10%, and 17% at the apex, apical septum and mid-septum respectfully (p=0.013). Baseline LVEF was comparable (LP: 56±7% vs TVP: 58±4%, p=0.103). Paced QRS duration was comparable (LP: 167±29 ms vs TVP: 158±17 ms, p=0.225). At baseline, RV and LV GLS were comparable [(RV pre: LP -17.6±4.9% vs TVP -16.7±4.8%, p=0.505), (LV pre: LP -16.1±2.4% vs TVP -15.6±3.6%, p=0.639)]. However, after pacemaker implantation, RV GLS was comparable, but LV GLS was significantly less impaired with LP vs TVP [(RV post: LP -17.1±5.2% vs TVP -15.4±3.4%, p=0.176), (LV post: LP -15.9±2.2% vs TVP -13.2±3.5%, p=0.002)]. The change in RV GLS was comparable, but the change in LV GLS indicated significantly less impairment with LP vs TVP [(RV change: LP 0.6±5.7% vs TVP 1.3±4.9%, p=0.631), (LV change: LP 0.2±1.8% vs TVP 2.5±4.3%, p=0.015)]. Significantly fewer patients developed PICM with LP vs TVP (LP: 1 (5%) vs TVP: 8 (28%) patients, p=0.032).
Conclusions: In pacemaker dependent patients, the incidence of PICM was lower with LP vs TVP. Despite a similar baseline LV GLS, patients with LP vs TVP had significantly better LV GLS post-pacemaker implant. Ventricular dyssynchrony, as assessed by GLS, may explain the higher incidence of PICM in this population.
